

TOOTH REMOVAL / EXODONTIA
Tooth removal, also known as dental extraction, is the removal of teeth from the dental alveolus in the alveolar bone. Extractions are performed for a wide variety of reasons, but most commonly 1 to remove teeth which have become unrestorable through tooth decay, periodontal disease, or dental trauma, especially when they are associated with toothache.
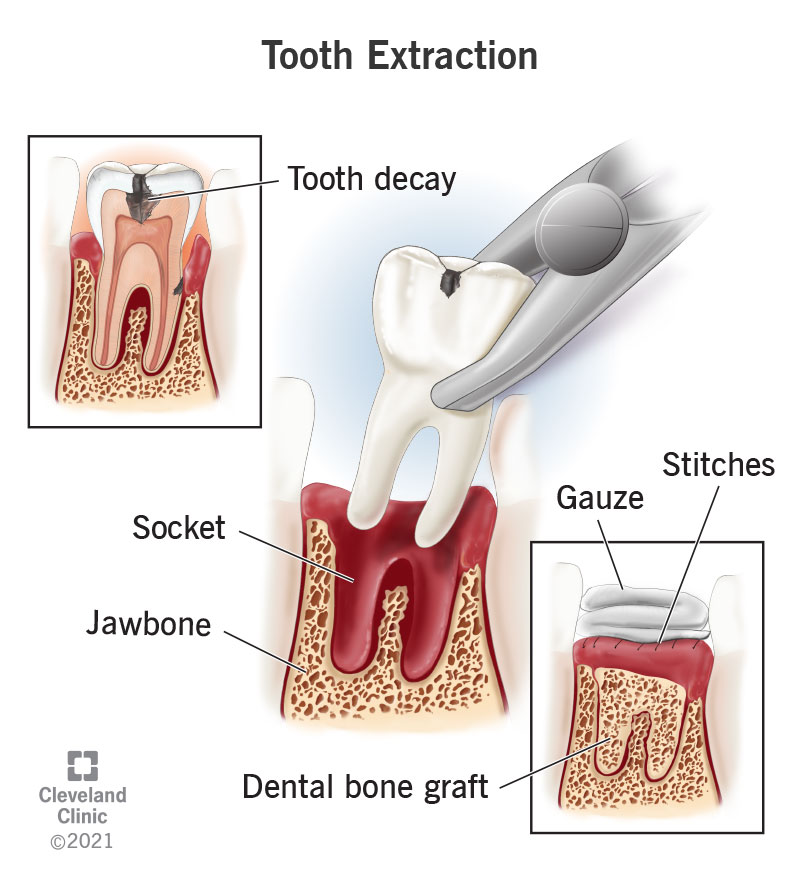
Exodontia is the technical term for tooth extraction. It's a procedure where a tooth is removed from its socket in the jawbone. Here's what you need to know about tooth extraction:
Reasons for Exodontia
Tooth Decay: Severe tooth decay that can't be treated with fillings or crowns. Gum Disease: Advanced gum disease that weakens the bone and soft tissues supporting the tooth. Impacted Teeth: Teeth that are unable to erupt properly due to overcrowding or other obstacles. Preparation for Orthodontic Treatment: To create space for other teeth to move into proper alignment. Injury or Trauma: Fractured or damaged teeth that can't be repaired.The Procedure
Exodontia is typically performed by a dentist or oral surgeon under local anesthesia. In some cases, general anesthesia or sedation may be used, especially for complex extractions or anxious patients.
Types of Extractions
Simple Extraction: A straightforward removal of a tooth that is visible and easily accessible. Surgical Extraction: A more complex procedure for impacted teeth or those that are partially or completely covered by gum tissue. WISDOM TOOT EXTRACTIONWISDOM TOOTH REMOVAL
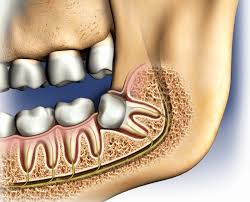
Wisdom teeth, also known as third molars, are the last adult teeth to erupt in the mouth. They typically begin to emerge between the ages of 17 and 21. However, sometimes there isn't enough room in the jaw for these teeth to grow properly, leading to a variety of problems.
Common problems associated with wisdom teeth:
Impaction: Wisdom teeth may become impacted, meaning they fail to fully erupt through the gums. This can cause pain, swelling, and infection.
Crowding: Impacted wisdom teeth can cause crowding of other teeth, leading to misalignment and potential bite problems.
Cysts and tumors: In some cases, impacted wisdom teeth can lead to the development of cysts or tumors.
Gum disease: Wisdom teeth can be difficult to clean, making them prone to gum disease.
When is wisdom tooth removal necessary?
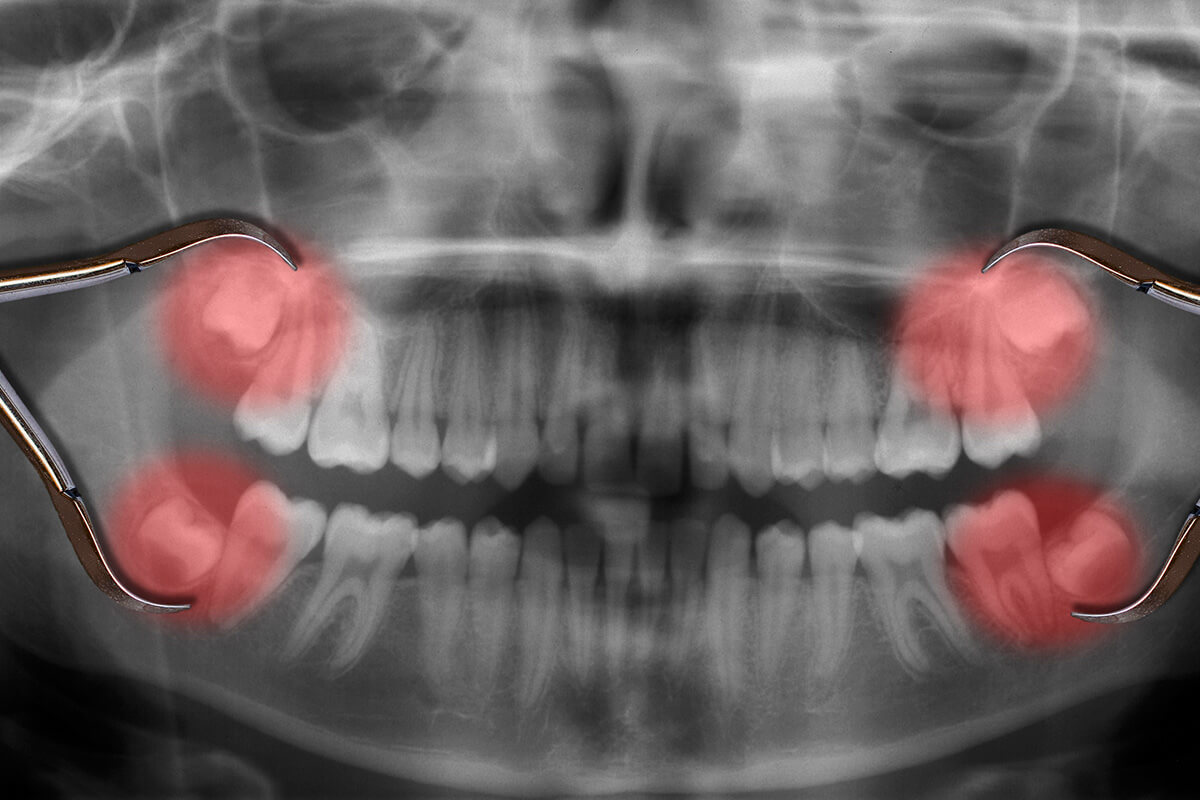
Your dentist or oral surgeon may recommend wisdom tooth removal if you experience any of the following:
Severe pain: Persistent pain or discomfort in the back of your mouth.
Infection: Signs of infection, such as swelling, redness, or pus.
Damage to adjacent teeth: Wisdom teeth can damage the roots of nearby teeth.
Cyst or tumor formation: If a cyst or tumor develops around an impacted wisdom tooth.
Difficulty cleaning: If you have difficulty keeping your wisdom teeth clean, leading to gum disease.
The wisdom tooth removal procedure:
Wisdom tooth removal is a common surgical procedure performed under local or general anesthesia. The dentist or oral surgeon will make an incision in the gum tissue to access the tooth and then remove it. In some cases, the tooth may need to be sectioned into smaller pieces for easier removal.
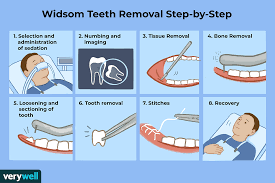
Recovery from wisdom tooth removal:
Recovery time varies depending on the complexity of the surgery and individual healing rates. Here are some general tips for a smooth recovery:
Rest: Avoid strenuous activity and get plenty of rest.
Ice packs: Apply ice packs to the affected area to reduce swelling.
Soft foods: Stick to soft foods like soups, mashed potatoes, and yogurt.
Avoid smoking and alcohol: These can slow down the healing process.
Oral hygiene: Gently rinse your mouth with warm salt water to keep the area clean.
Pain management: Take over-the-counter pain medication as directed by your dentist or oral surgeon.
If you experience severe pain, excessive bleeding, or signs of infection, contact your dentist or oral surgeon immediately.
Remember, this is general information, and it's essential to consult with a dental professional for personalized advice and treatment.
Recovery
After the extraction, there may be some discomfort, swelling, and bleeding. Your dentist will provide you with specific instructions for caring for your mouth and managing any side effects.
Important Considerations
Risks and Complications: While generally safe, exodontia can have potential risks such as infection, dry socket, or damage to nearby teeth or nerves. Alternative Treatments: Your dentist will always explore other options for saving your tooth before recommending extraction.If you have any concerns about exodontia, it's essential to consult with a qualified dentist or oral surgeon. They can assess your individual situation and recommend the best course of treatment.
